The Definitive Guide to STEAM Education: Transforming Learning through Hands-On Experiences
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving world, the need for STEM education has never been greater. However, more and more educators are supplementing this type of science and engineering curriculum with arts - which can lead to a more comprehensive and diverse learning experience. This guide delves into the concept of STEAM education, an educational approach known for its unique ability to combine STEM with the Arts. Not only does this approach boost students' creativity and real-world problem-solving skills, but it facilitates the type of hands-on learning experiences that prepare students for a variety of future careers.
Understanding STEM Education
STEM education focuses on the core disciplines of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. While these disciplines were traditionally studied in isolation, in 2001 the US National Science Foundation introduced the acronym STEM to better explain the type of integrated science learning that would prepare students for in-demand careers. (Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2023).
The Emergence of STEAM Education
After the STEM education framework became popular in the 2000s, teachers began to recognize the importance of incorporating creativity into the mix. Subjects like the visual arts, theater, design and music could be essential in driving the type of creativity needed for students to understand complex concepts and solve real-world engineering problems.
STEAM education was therefore born – incorporating the Arts with traditional STEM education.
Benefits of STEAM Education
Holistic Learning: While traditional forms of education focus on one single discipline, delving deeply into an area of knowledge using methods that are well established – STEAM education encourages students to approach problems from multiple perspectives. A student might combine data science with mechanical engineering and chemistry to see a project to completion. This way of learning has enormous benefits for students, as they tackle problems in the same way they would be expected to by an employer – using all the skills at their disposal to drive innovation and find solutions to real-world problems.
Real-World Applications: Through applying skills gained in a variety of disciplines to solve a real-world problem – students gain the type of practical, hands-on experience employers place considerable value on. Theory is integrated with application – meaning students don’t just learn the fundamentals of hydrogen chemistry, for example, but learn how to meaningfully apply this theory in solving real-world engineering problems.
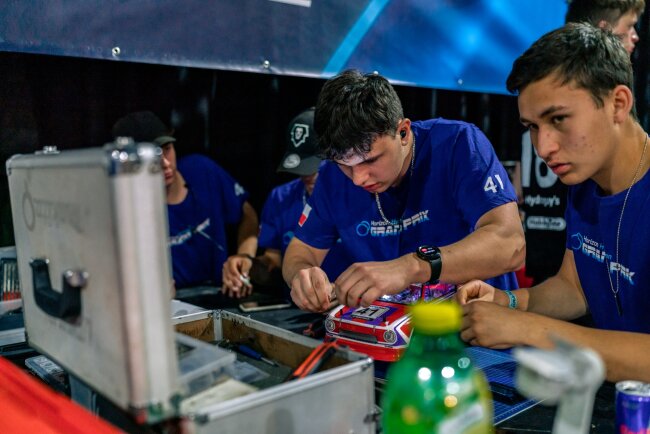
One example of this process in action is high school students designing, engineering, constructing and racing fuel cell electric cars powered by hydrogen. Students must not only learn the theory behind mechanical engineering, hydrogen chemistry and data science – but they learn to apply this knowledge practically in creating the perfect hydrogen-powered car capable of competing globally.
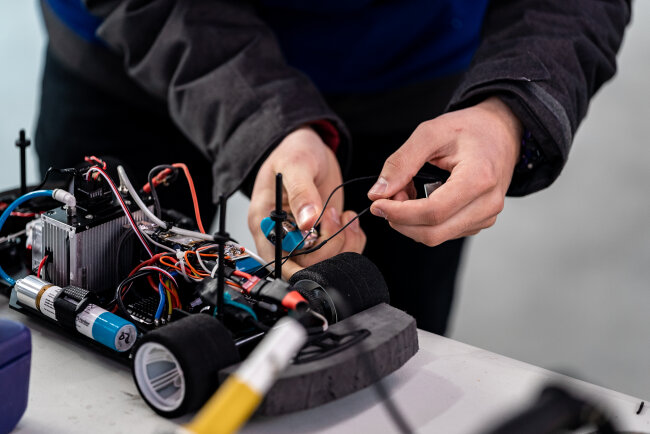

Collaboration and Communication: Through encouraging students to work together and solve problems collectively, STEAM education promote teamwork, communication, and effective collaboration – skills employers place considerable value on. Often this takes the form of students with strengths in different disciplines applying their knowledge collectively. While one student may love chemistry, another may excel in mechanical engineering. Through being challenged to work on a project together, these students learn how to collaborate and develop vital communication skills employers greatly value.
Improved Engagement: Students find STEAM education projects incredibly fun. As opposed to learning from a textbook and memorizing facts, students are given the opportunity to take ownership of their learning by deploying knowledge gained from the classroom in real-world applications. Often projects have an element of competition – such as fuel cell electric car racing – which can significantly boost levels of engagement among students.
Implementing STEAM Education
How can you implement STEAM education in your classroom?
While STEAM education has enormous benefits for students, integrating this educational approach into school curriculums can be incredibly challenging for teachers. With budgets often tight, resources limited, and traditional ways of learning entrenched – teachers need the guidance, support, and know-how in order to implement STEAM education in a meaningful way. Here’s how to do it:
Curriculum Integration: One of the best ways to integrate the Arts into STEM education is by assigning projects that have a creative element. While building and constructing a hydrogen-powered car may develop essential STEM skills such as mechanical engineering and data science – integrating the ability to create visual representations on the car body or designing prototypes is a fantastic way of incorporating the Arts into STEM education.
Partnerships: STEAM education projects often demand costly resources, and this cost can be a significant barrier for students looking to participate. Luckily, a variety of organizations from around the world sponsor schools to take part in STEAM activities. These partnerships between industry and education enable students to not only gain access to opportunities to integrate science and engineering with the arts, but it opens up the possibility for economic advancement among those who face disadvantages.
Example of Successful STEAM Education Initiatives
The Hydrogen Grand Prix is an example of a successful STEAM education initiative in which students gain the opportunity to design, engineer, construct and race a hydrogen-powered 1:10 scale car against the best teams worldwide. A six-month dedicated curriculum is enhanced by real-world engineering activities – and students integrate creative design, mechanical engineering, data science, hydrogen chemistry and much more in perfecting their self-built hydrogen car. The initiative is currently in 20+ countries around the world with over 20,000 students participating.
Conclusion
STEAM education offers significant advantages over traditional education approaches. Holistic learning, real-world applications, collaboration and communication and improved engagement can transform classroom environments. And while this transformation of learning experience can be difficult to access for all communities – strong partnerships between schools and industry enable STEAM education to become accessible to all.
Interested in bringing STEAM educational experiences to your school? Learn about the Hydrogen Grand Prix program today.

